The Bloom’s Taxonomy was created in 1956 by Dr Benjamin Bloom. It is the classification of learning objectives Bloom’s three learning domain of education. There are cognitive domain which is related to knowledge, affective domain which is related to attitude and psychomotor domain which is related to skills. Cognitive domain consider as the skills like knowledge, comprehension and thinking etc. There are six categories of cognitive domain in taxonomy that is knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, evolution. The stages develop as recall data and information, understand it and apply it to new situation, examine information and compile it, final stage is about justify the information. Knowledge is the result of thinking and comprehension and synthesis reflect the nature of thinking.
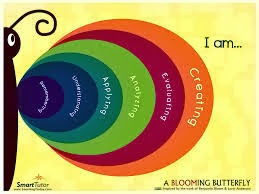
Lorin Anderson, a
former student of Bloom, revisited the cognitive domain in the learning
taxonomy in 1990s.
As the taxonomy reflects different forms of thinking and thinking is an active
process verbs were used rather than nouns. He changed the name of six categories as remembering,
understanding, applying, analysing, evaluating, and creating. It listed in
order below, starting from the simplest behaviour to the most complex. The
revisited taxonomy generally focuses on the thinking. The first three
categories is lower level thinking and last three categories is higher level
thinking. This leads to the simple thinking to critical thinking for the
particular topic. The six stages are help learners to achieve the goal in
thinking process.
No comments:
Post a Comment